Table Of Content

The pictures of ingrown hairs don’t match perfectly, and the images of genital herpes leave her with more questions than answers. Conflicted and concerned, especially with no knowledge of her new partner’s STD status, she turns to an online dermatology consultation in search of answers. If you have problems with ingrown facial hair, switching from a razor to a hair removal cream may provide relief. Depilatories are creams and lotions designed specifically to remove unwanted hair, even on sensitive parts of your body like the bikini line and face.
Avoiding irritation
If you’re waxing facial hair, apply a warm compress to your face a few minutes before applying the wax. Shaving is the most common type of hair removal people do at home, and improper technique is often the culprit of razor bumps and razor burn. To help you avoid both, here are some expert tips to ensure you’re shaving correctly. If you get ingrowns on your face (especially after shaving facial hair), experts recommend opting for a gentle acne face wash like this one from Neutrogena, which contains salicylic acid. The wash has a jelly consistency when it comes out of the pump, but it gets foamy as you massage it into your skin with your fingers or a facial cleansing brush, in my experience.
What questions should I ask my healthcare provider?
Within just two days of use, the red bumps that had plagued me for years were significantly reduced. Laser hair removal is a safe and effective method that can be performed on any area of the body (except around the eyes). A technician applies a pulse of light onto the surface of the skin, killing not just the hair but the entire hair follicle. With any luck, you’ll be able to get the edge of the hair out so that it doesn’t continue to grow under the skin. If you’re able to do so, complete the process by washing and exfoliating the area thoroughly.
Using tweezers
These symptoms often occur alongside the formation of clusters of fluid-filled blisters and sores, which can cause significant discomfort and distress. These can be on your buttocks, thighs, or rectal area or along your genitals. Rarely, blisters may form in the urethra, where urine leaves the body [5]. Some extra hair growth may occur in those who have higher than average levels of sex hormones [3]. But if it doesn’t, you could have an infection (which can cause pus to form), darkened skin, scarring, pain or itching.
Exactly How to Shave Pubic Hair Safely If You Have a Vagina SELF - Self
Exactly How to Shave Pubic Hair Safely If You Have a Vagina SELF.
Posted: Mon, 21 Aug 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
When this happens, the hair in the follicle can become stuck or grow sideways into the skin, causing an ingrown hair. In some cases, the hair can be seen growing under the surface of the skin. Preventing ingrown hairs can often be managed at home, though there are times when a visit to the doctor may be appropriate. Hair structure and direction of growth play a role in ingrown hair. A curved hair follicle, which produces tightly curled hair, is believed to encourage the hair to reenter the skin once the hair is cut and starts to grow back. Shaving creates a sharp edge on hair, making it easier to pierce the skin.
selectHow to remove blackheads at home
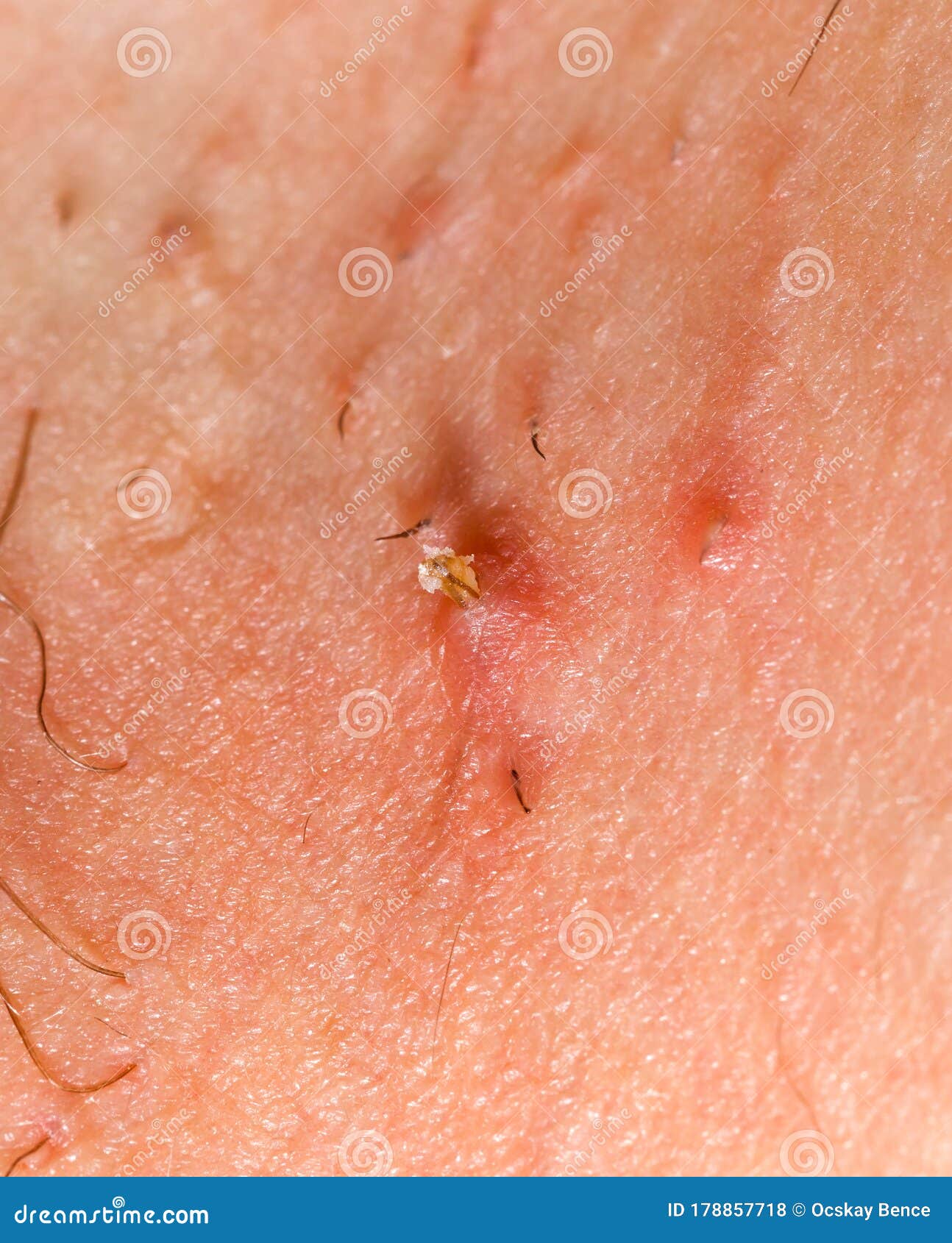
“This is called a pustule and occurs because there is a buildup of bacteria, or an infection,” adds Dr. Lolis. The bacteria can come from what’s naturally on the surface of the skin, or you may drag bacteria into a razor bump if you pick at it or try to dig it out on your own, says Dr. Wechsler. “Don’t try to pop them and don’t try to pick them,” she warns.
How do you remove an ingrown hair?
Instead, a hair keeps growing, but under the skin, either in a curl, in a downward direction, or to the side under the surface of the skin. Usually an ingrown hair looks like a red bump, but sometimes you can see the hair through the skin, and it may have a white pus-filled head. Sometimes, dead skin can clog a hair follicle, which forces the hair to grow sideways under your skin rather than up and out. If you cut naturally curly hair too short, the sharpened end of the hair can pierce your skin, causing an ingrown hair. An ingrown hair is one that's grown back into your skin instead of rising up from it.
The brushes have an ergonomic, easy-to-hold grip and can be used on different hair textures ranging from fine and thin to thick, coarse, and curly. The fine bristles are great for wet and dry exfoliation so you can get rid of razor bumps and ingrown hairs as quickly as possible. No, you should never pop, pick, pluck or pull at an ingrown hair, our experts unanimously agreed. Doing so can make ingrowns worse and prolong the healing process. Some prescription medications can help prevent ingrown hairs.
What Does an Ingrown Hair Cyst Look Like?
When you have thick or curly hair, you can get a type of ingrown hair called pseudofolliculitis. The hair that grows back has a sharper edge, so it can more easily poke back through your skin and get trapped under the surface. If you shave, tweeze, or wax your hair, you can develop ingrown hairs.
It can be applied all over the body to any area that typically develops ingrown hairs, including the pubic area. To help cool down any irritation or redness, this serum includes several popular calming ingredients like vitamin E, chamomile, and lavender. However, those with naturally curly or wavy, thick and coarse hair are the most prone to ingrowns, Weinstein says. Curly and wavy hair is more likely to curl into the skin compared to straight hair. Signs of ingrown hairs include bumps that appear like acne, tenderness, redness, and itching. After healing, ingrown hairs can leave behind keloids (scarring) and areas of hyperpigmentation (skin discoloration).
Most instances of ingrown hair get better without treatment. You can avoid this condition by not removing hair or not shaving very close to the skin. If that's not an option, you might try other hair removal methods that lessen the risk of developing ingrown hair. In rare cases, your healthcare provider may use a sterile surgical knife with a thin blade (scalpel) to make a small cut in your affected areas. They’ll squeeze out any pus and use sterile tweezers to remove the ingrown hair.
Keep reading to learn how to recognize an infected ingrown hair, as well as tips for treating and preventing them. An infected ingrown hair happens when a hair is blocked from leaving the skin or newly emerged hair curls back into the skin, and the follicle becomes infected. If the deep ingrown hair is giving you a lot of trouble and lasts more than a couple of weeks, it's a good idea to see a doctor.
Don’t pluck it out completely — just coax it out so that the edge of the hair is above the surface layer of the skin. Sometimes, they can even cause a deep and painful infection under the skin. The form of treatment will likely rely on your personal preference. Do you prefer a cream that you can rub in or a more liquid option that you can quickly apply with a cotton swab?